Planet Python
Last update: February 26, 2026 09:43 PM UTC
February 26, 2026
Real Python
Quiz: Hands-On Python 3 Concurrency With the asyncio Module
This quiz sharpens your intuition for Python’s asyncio module. You’ll decide when async is the right tool, see how the event loop schedules work, and understand how coroutines pause and resume around I/O.
Along the way, you’ll revisit async and await, coroutine creation, async generators, asyncio.run(), and concurrent execution with asyncio.gather(). For a quick refresher before you start, check out Hands-On Python 3 Concurrency With the asyncio Module.
[ Improve Your Python With 🐍 Python Tricks 💌 – Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. >> Click here to learn more and see examples ]
February 26, 2026 12:00 PM UTC
Graham Dumpleton
Deploying Educates yourself
In my last post I showed how an AI skill can generate a complete interactive workshop for the Educates training platform. The result was a working workshop for the Air Python web framework, and you can browse the source in the GitHub repository. But having workshop source files sitting in a repository is only half the story. The question that naturally follows is: how do you actually deploy it?
If you've used platforms like Killercoda, Instruqt, or Strigo, the answer would be straightforward. You push your content to the platform, and it handles the rest. But that convenience comes with a trade-off that's easy to overlook until it bites you.
Not another SaaS platform
The interactive workshop space has been dominated by SaaS offerings. Katacoda was one such option, but when it shut down in 2022, a lot of people lost workshops they'd invested significant time in creating. Killercoda emerged as a successor, but the fundamental dynamic is the same: you're reliant on a third party. Instruqt and Strigo are commercial services where you pay for access and have no control over how the platform evolves, what it costs next year, or whether it continues to exist at all.
Educates takes a different approach. It's open source and self-hosted. You deploy it on your own infrastructure, which means you decide where it runs, when it runs, and who has access. Whether you're running private internal training for your team or hosting public workshops at a conference, you own the platform. If you want to modify how it works, you can. If you want to run it air-gapped inside a corporate network, you can do that too. That freedom is the point.
Deploy it where you want
Because you're deploying Educates yourself, you get to choose the infrastructure. Educates runs on Kubernetes, and that Kubernetes can live anywhere. You could use a managed cluster from a cloud provider like AWS, GCP, or Azure. You could run your own Kubernetes on virtual machines or physical hardware. Or, if you just want to try things out on your own machine, the Educates CLI can create a local Kubernetes cluster for you using Kind running on Docker.
That range of options means you can go from personal experimentation to production training without switching platforms. The same workshop content works regardless of where the cluster is running.
For the rest of this post I'll walk through that local option, since it's the easiest way to get started and doesn't require any cloud infrastructure.
Creating a local Educates environment
The Educates CLI handles the setup. If you have Docker running on your machine, creating a local Educates environment is a single command:
educates create-cluster
This creates a Kind-based Kubernetes cluster and installs everything Educates needs on top of it: the platform operators that manage workshop sessions, a local container image registry, and ingress routing so you can access workshops through your browser. It takes a few minutes to complete, but once it's done you have a fully functional Educates installation running locally.
Publishing and deploying a workshop
With the local environment running, you can publish the Air workshop from a local checkout of the GitHub repository. From the workshop directory, run:
educates publish-workshop
This builds an OCI image containing the workshop files and pushes it to the local image registry that was set up alongside the cluster. The workshop definition file (which the AI skill created as part of the workshop in my previous post) already contains everything Educates needs to know about how to deploy and configure the workshop, so there's nothing else to set up.
To deploy the workshop so it's available to use, run:
educates deploy-workshop
That's it. The workshop is now running on your local Educates installation and ready to be accessed.
Accessing the workshop
To open the training portal in your browser, run:
educates browse-workshops
This opens the Educates training portal, which is where learners go to find and start workshops.
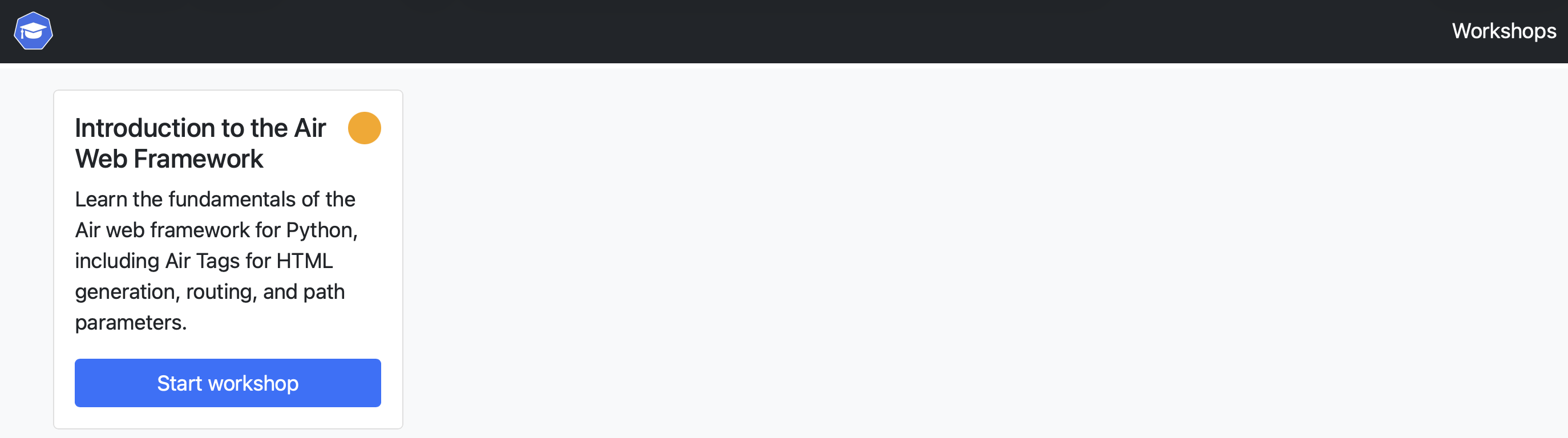
From the portal, you select the workshop you want to run and click to start it. Educates spins up an isolated session for you, and after a moment you're dropped into the workshop dashboard.
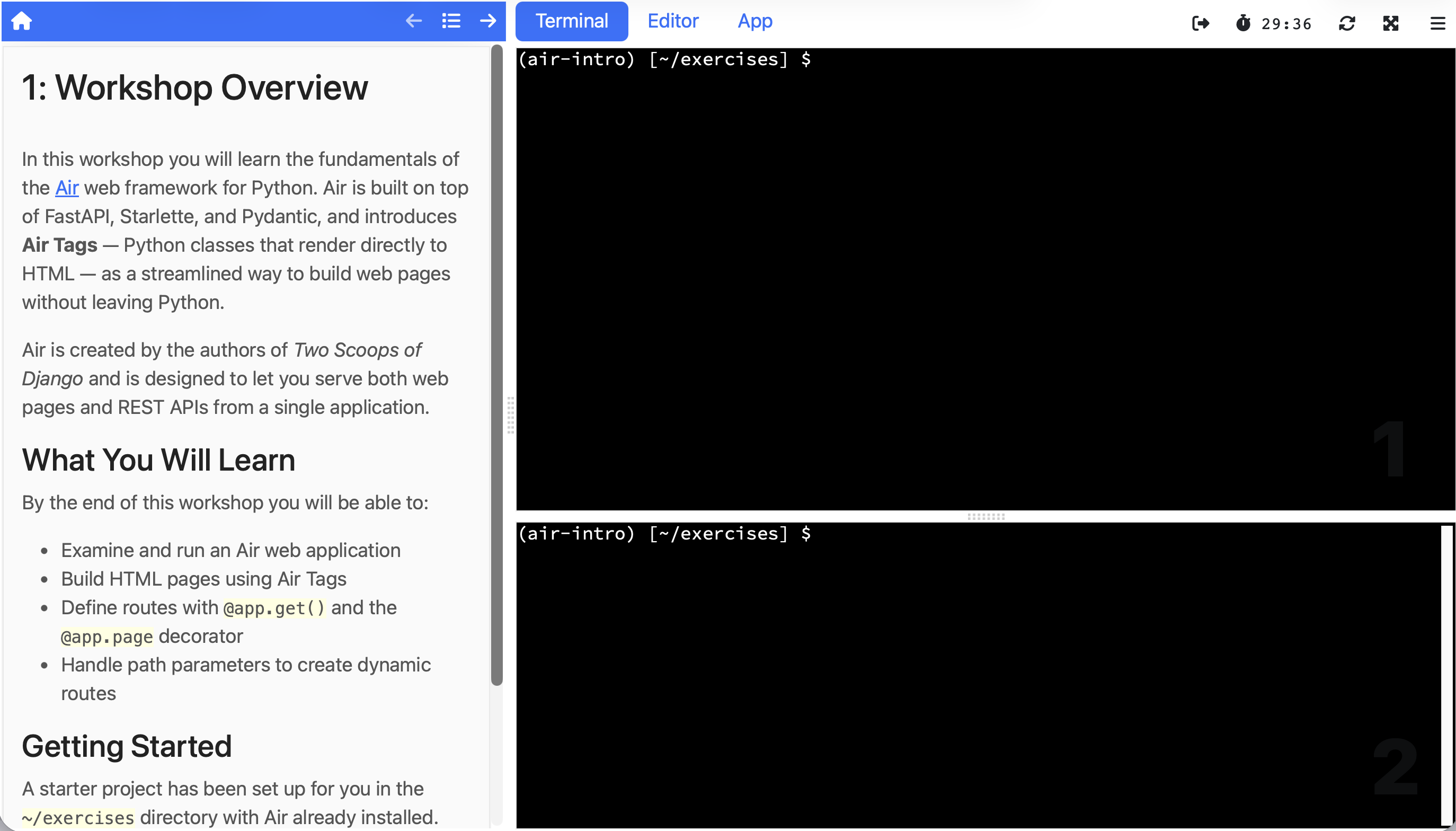
The dashboard is the full Educates workshop experience. On one side you have the workshop instructions with their clickable actions. On the other side is the integrated environment with a terminal and editor, plus any additional dashboard tabs the workshop has configured (in this case, a browser tab for viewing the running web application). Everything the learner needs is right there, and it's all running on your own machine.
The workshop I showed being generated in the last post works exactly as expected. You can click through the instructions, run the commands, edit the files, and see the Air web application running in the embedded browser tab. The entire guided experience functions just as it would on a production Educates installation.
Beyond Kubernetes
Running Educates on a local Kubernetes cluster is the most straightforward way to try things out, and it gives you the complete platform experience. But Kubernetes isn't the only option for running a workshop. The same underlying container image used to run the workshop can also be run directly in Docker without any Kubernetes cluster at all. The Educates CLI supports this too.
That said, running in Docker comes with trade-offs. Some features that depend on Kubernetes won't be available, and the workshop itself may need adjustments to work correctly in a Docker environment. I'll cover that in a future post, including how the AI skill from the previous post can help figure out what needs to change.
If you want to try any of this yourself, the Educates documentation has a more detailed quick start guide that covers installation and configuration options beyond what I've shown here.
February 26, 2026 10:38 AM UTC
PyPodcats
Episode 11: With Sheena O'Connell
Learn about Sheena's journey. Sheena is a software engineer with high passion for education. She built an alternative education systems with deep expertise in effective teaching and educator development. She is a founder of Prelude.techLearn about Sheena's journey. Sheena is a software engineer with high passion for education. She built an alternative education systems with deep expertise in effective teaching and educator development. She is a founder of Prelude.tech
We interviewed Sheena O’Connell.
Sheena began her career as a software engineer and technical leader across multiple startups, but her passion for education led her to spend the last five years reimagining how people learn to code professionally. Working within the nonprofit sector, she built alternative education systems from the ground up and developed deep expertise in effective teaching, educator development, and the structural limitations of traditional education models. Sheena is the founder of Prelude.tech, where she delivers rigorous technical training alongside consultation and coaching for technical educators and organizations with education functions. She also leads the Guild of Educators, a community she founded to empower technology educators through shared resources, support, and evidence-based teaching practices.
In this episode, Sheena O’Connell tells us about her journey, the importance of community and good practices for teachers and educators in python, organizational psychology and how herself has become involve in this journey. We talk about how to enable a 10 x team and how to enable the community through guild of educators.
Topic discussed
- Introductions
- Getting to know Sheena
- Her involvement in the community
- Sheena’s journey and her passion for education
- Re-implementing effective education system for learning how to code professionaly in python
- Importance of communiy
- Organizational psychology
- PyCon Africa cool badges
Links from the show
- guild of educators: https://guildofeducators.org/
February 26, 2026 09:00 AM UTC
February 25, 2026
Python Morsels
Lexicographical ordering in Python
Python lexicographically orders tuples, strings, and all other sequences, comparing element-by-element.
String ordering
Is the string "apple" greater than the string "animal"?
>>> "apple" > "animal"
When I ask this question to a roomful of Python developers, I often see folks mouth L-M-N-O-P.
The word "animal" comes before "apple" in alphabetical ordering.
So "apple" is greater than "animal":
>>> "apple" > "animal"
True
Strings in Python are ordered alphabetically. Well, sort of.
Uppercase "Apple" is less than lowercase "apple":
>>> "Apple" < "apple"
True
And we can also order characters that are not in the alphabet.
For example, the dash character (-) is less than the underscore character (_):
>>> '-' < '_'
True
Each character in a Python string has a number associated with it. These numbers are the Unicode code points for these characters:
>>> [ord(c) for c in "apple"]
[97, 112, 112, 108, 101]
>>> [ord(c) for c in "animal"]
[97, 110, 105, 109, 97, 108]
Python essentially uses alphabetical ordering.
But the alphabet it uses consists of every possible character, and the order of those characters comes from their Unicode code points.
I don't recommend memorizing the Unicode code points of each character.
Instead, I would lowercase your strings as you order them. And keep in mind that every character counts when you're ordering strings, even non-alphabetical ones.
Lexicographical ordering
Lexicographical ordering is a fancy …
Read the full article: https://www.pythonmorsels.com/lexicographical-ordering/
February 25, 2026 03:45 PM UTC
Real Python
How to Run Your Python Scripts and Code
Running Python scripts is essential for executing your code. You can run Python scripts from the command line using python script.py, directly by making files executable with shebangs on Unix systems, or through IDEs and code editors. Python also supports interactive execution through the standard REPL for testing code snippets.
This tutorial covers the most common practical approaches for running Python scripts across Windows, Linux, and macOS.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll understand that:
- The
pythoncommand followed by a script filename executes the code from the command line on all operating systems. - Script mode runs code from files sequentially, while interactive mode uses the REPL for execution and testing with immediate feedback.
- Unix systems require executable permissions and a shebang line like
#!/usr/bin/env python3to run scripts directly as programs. - The
pythoncommand’s-moption runs Python modules by searchingsys.pathrather than requiring file paths. - IDEs like PyCharm and code editors like Visual Studio Code provide built-in options to run scripts from the environment interface.
To get the most out of this tutorial, you should know the basics of working with your operating system’s terminal and file manager. It’d also be beneficial to be familiar with a Python-friendly IDE or code editor and with the standard Python REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop).
Free Download: Get a sample chapter from Python Tricks: The Book that shows you Python’s best practices with simple examples you can apply instantly to write more beautiful + Pythonic code.
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “How to Run Your Python Scripts” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
How to Run Your Python ScriptsOne of the most important skills you need to build as a Python developer is to be able to run Python scripts and code. Test your understanding on how good you are with running your code.
What Scripts and Modules Are
In computing, the term script refers to a text file containing a logical sequence of orders that you can run to accomplish a specific task. These orders are typically expressed in a scripting language, which is a programming language that allows you to manipulate, customize, and automate tasks.
Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled. So, scripts are typically run by an interpreter, which is responsible for executing each order in a sequence.
Python is an interpreted language. Because of that, Python programs are commonly called scripts. However, this terminology isn’t completely accurate because Python programs can be way more complex than a simple, sequential script.
In general, a file containing executable Python code is called a script—or an entry-point script in more complex applications—which is a common term for a top-level program. On the other hand, a file containing Python code that’s designed to be imported and used from another Python file is called a module.
So, the main difference between a module and a script is that modules store importable code while scripts hold executable code.
Note: Importable code is code that defines something but doesn’t perform a specific action. Some examples include function and class definitions. In contrast, executable code is code that performs specific actions. Some examples include function calls, loops, and conditionals.
In the following sections, you’ll learn how to run Python scripts, programs, and code in general. To kick things off, you’ll start by learning how to run them from your operating system’s command line or terminal.
How to Run Python Scripts From the Command Line
In Python programming, you’ll write programs in plain text files. By convention, files containing Python code use the .py extension, and there’s no distinction between scripts or executable programs and modules. All of them will use the same extension.
Note: On Windows systems, the extension can also be .pyw for those applications that should use the pythonw.exe launcher.
To create a Python script, you can use any Python-friendly code editor or IDE (integrated development environment). To keep moving forward in this tutorial, you’ll need to create a basic script, so fire up your favorite text editor and create a new hello.py file containing the following code:
hello.py
print("Hello, World!")
This is the classic "Hello, World!" program in Python. The executable code consists of a call to the built-in print() function that displays the "Hello, World!" message on your screen.
With this small program in place, you’re ready to learn different ways to run it. You’ll start by running the program from your command line, which is arguably the most commonly used approach to running scripts.
Using the python Command
To run Python scripts with the python command, you need to open a command-line window and type in the word python followed by the path to your target script:
Read the full article at https://realpython.com/run-python-scripts/ »
[ Improve Your Python With 🐍 Python Tricks 💌 – Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. >> Click here to learn more and see examples ]
February 25, 2026 02:00 PM UTC
February 24, 2026
Django Weblog
Google Summer of Code 2026 with Django
When we learned that the Django Software Foundation has been accepted as a mentoring organization for Google Summer of Code 2026, it marked another steady milestone in a long-standing relationship. Django first participated in GSoC in 2006, and 2026 represents our 21st consecutive year in the program.
Over two decades, GSoC has become a consistent pathway for contributors to engage more deeply with Django — not just through a summer project, but often through continued involvement that extends well beyond the official coding period.
For many of you reading this, this might be your first exposure to how Django’s open source ecosystem works. So before we get into applications and expectations, let’s take a step back and understand the environment you’re stepping into.
Understanding the Django Ecosystem
The Django Software Foundation (DSF) is the non-profit organization that supports the long-term sustainability of Django. Django itself is developed entirely in the open. Feature discussions, architectural debates, bug reports, design proposals, and code reviews all happen publicly.
That openness is intentional. It allows anyone, from anywhere in the world, to participate. But it also means decisions are rarely made quickly or casually. Changes are discussed carefully. Trade-offs are evaluated. Backwards compatibility is taken seriously.
If you are new, it helps to understand the main spaces where this work happens:
- The Django Forum is where broader discussions take place — new feature ideas, design direction, and community conversations.
- Django Trac is the issue tracker, where bugs, feature requests, and patches are formally recorded and reviewed. If no one is working on an issue, you can assign it yourself and start working on it.
- Code contributions happen through pull requests, where proposed changes are reviewed, tested, and discussed in detail before being merged.
- New features are proposed and discussed in the new-features repository. There is a project board view that shows the state of each proposal.
For someone new, this ecosystem can feel overwhelming at first. Threads may reference decisions made years ago. Review comments can be detailed. Standards are high.
That is precisely why GSoC matters to us. It provides a structured entry point into this culture, with mentorship and guidance along the way, helping contributors understand not just how to write code — but how Django evolves.
Why the Django Forum Is Central
Most GSoC journeys in Django begin on the Django Forum — the community’s public space for technical discussions about features, design decisions, and improvements to Django.
Introducing yourself there is not a formality; it is often your first real contribution. When you discuss a project idea publicly, you demonstrate how you think, how you respond to feedback, and how you handle technical trade-offs. Questions and challenges from mentors are not barriers — they are part of the collaborative design process.
Proposals that grow through open discussion on the Forum are almost always stronger than those written in isolation.
What To Do
If you are planning to apply for GSoC 2026 with Django, here is what we strongly encourage:
Start early.
Do not wait until the application window opens. Begin discussions well in advance.
Engage publicly.
Introduce yourself on the Forum. Participate in ongoing threads. Show consistent involvement rather than one-time activity.
Demonstrate understanding(very important)
Read related tickets and past discussions. Reference them in your proposal. Show that you understand the technical and philosophical context.
Be realistic about scope.
Ambitious ideas are welcome, but they must be grounded in technical feasibility within the GSoC timeframe.
Show iteration.
If your proposal evolves because of feedback, that is a positive signal. It shows adaptability and thoughtful engagement.
What Not To Do
Equally important are the expectations around what we will not consider.
Do not submit a proposal without prior discussion.
A proposal that appears for the first time in the application form, without any Forum engagement, will be at a disadvantage.
Do not generate a proposal using AI and submit it as-is.
If a proposal is clearly AI-generated, lacks discussion history, and shows no evidence of personal understanding, it will be rejected. We evaluate your reasoning process, not just the surface quality of the document.
Do not copy previous proposals.
Each year’s context is different. We expect original thinking and up-to-date understanding.
Do not treat GSoC as a solo internship.
Django development is collaborative. If you are uncomfortable discussing ideas publicly or receiving detailed feedback, this may not be the right fit.
Do not submit empty or placeholder proposal documents.
In previous years, we have received blank or near-empty submissions, which create unnecessary effort for volunteer reviewers. Such proposals will not be considered.
Do not repeatedly tag or ping maintainers for reviews.
Once you’ve submitted your proposal or patch, give reviewers time to respond. Maintainers are volunteers managing many responsibilities, and repeated tagging does not speed up the process. Patience and respectful follow-ups (after a reasonable interval) are appreciated.
On AI Usage
We recognize that AI tools are now part of many developers’ workflows. Using AI to explore documentation, clarify syntax, or organize thoughts is not inherently a problem.
However, AI must not replace ownership.
You should be able to clearly explain your architectural decisions, justify trade-offs, and respond thoughtfully when challenged. If you cannot defend your own proposal without external assistance, it signals a lack of readiness for this kind of work.
The quality we look for is not perfect language — it is depth of understanding.
I’m a First-Time Contributor to Django — What Should I Do?
If this is your first time contributing to Django, start simple and start early.
First, spend some time understanding how Django works as an open source project. Read a few recent discussions on the Django Forum and browse open tickets to see the kinds of problems being discussed.
Next, introduce yourself on the Forum. Share your background briefly and mention what areas interest you. You don’t need to have a perfect project idea on day one — curiosity and willingness to learn matter more.
Then:
- Read the official first time contributor guide carefully.
- Try setting up Django locally and run the test suite.
- Look for small tickets on trac (including documentation or cleanup tasks) to understand the workflow.
- Ask questions on the Forum or in Discord if something is unclear.
Most importantly, be patient with yourself. Django is a mature and widely used framework, and it takes time to understand its design principles and contribution standards.
Strong contributors are not the ones who know everything at the start — they are the ones who show up consistently, engage thoughtfully, and improve through feedback.
To conclude
We are excited to welcome a new group of contributors into the Django ecosystem through Google Summer of Code 2026. We look forward to thoughtful ideas, constructive discussions, and a summer of meaningful collaboration — built not just on code, but on understanding and shared responsibility.
February 24, 2026 09:58 PM UTC
PyCoder’s Weekly
Issue #723: Chained Assignment, Great Tables, Docstrings, and More (Feb. 24, 2026)
#723 – FEBRUARY 24, 2026
View in Browser »
Chained Assignment in Python Bytecode
When doing chained assignment with mutables (e.g. a == b == []) all chained values get assigned to a single mutable object. This article explains why this happens and what you can do instead.
ROHAN PRINJA
Great Tables: Publication-Ready Tables From DataFrames
Learn how to create publication-ready tables from Pandas and Polars DataFrames using Great Tables. Format currencies, add sparklines, apply conditional styling, and export to PNG.
CODECUT.AI • Shared by Khuyen Tran
Replay: Where Developers Build Reliable AI

Replay is a practical conference for developers building real systems. The Python AI & versioning workshop covers durable AI agents, safe workflow evolution, and production-ready deployment techniques. Use code PYCODER75 for 75% off your ticket →
TEMPORAL sponsor
Write Python Docstrings Effectively
Learn to write clear, effective Python docstrings using best practices, common styles, and built-in conventions for your code.
REAL PYTHON course
Discussions
Python Jobs
Python + AI Content Specialist (Anywhere)
Software Engineer (Python / Django) (South San Francisco, CA, USA)
Articles & Tutorials
Join the Python Security Response Team!
The Python Security Response Team is a group of volunteers and PSF staff that coordinate and triage vulnerability reports and remediations. It is governed in a similar fashion to the core team. This article explains what the PSRT is and how you can join.
CPYTHON DEV BLOG
A CLI to Fight GitHub Spam
Hugo is a core Python maintainer and the CPython project gets lots of garbage PRs, not just AI slop but spam tickets as well. To help with this he has written a new GitHub CLI extension that makes it easier to apply a label to the PR and close it.
HUGO VAN KEMENADE
B2B MCP Auth Support

Your users are asking if they can connect their AI agent to your product, but you want to make sure they can do it safely and securely. PropelAuth makes that possible →
PROPELAUTH sponsor
Exploring MCP Apps & Adding Interactive UIs to Clients
How can you move your MCP tools beyond plain text? How do you add interactive UI components directly inside chat conversations? This week on the show, Den Delimarsky from Anthropic joins us to discuss MCP Apps and interactive UIs in MCP.
REAL PYTHON podcast
How to Use Overloaded Signatures in Python?
Sometimes a function takes multiple arguments of different types, and the return type depends on specific combinations of inputs. How do you tell the type checker? Use the @overload decorator from the typing module.
BORUTZKI
icu4py: Bindings to the Unicode ICU Library
The International Components for Unicode (ICU) is the official library for Unicode and globalization tools and is used by many major projects. icu4py is a first step at a Python binding to the C++ API.
ADAM JOHNSON
Evolving Git for the Next Decade
This article summarizes Patrick Steinhardt’s talk at FOSDEM 2026 that discusses the current shortcomings of git and how they’re being addressed, preparing your favorite repo tool for the next decade.
JOE BROCKMEIER
How to Install Python on Your System: A Guide
Learn how to install the latest Python version on Windows, macOS, and Linux. Check your version and choose the best installation method for your system.
REAL PYTHON
TinyDB: A Lightweight JSON Database for Small Projects
If you’re looking for a JSON document-oriented database that requires no configuration for your Python project, TinyDB could be exactly what you need.
REAL PYTHON
Django ORM Standalone: Querying an Existing Database
A practical step-by-step guide to using Django ORM in standalone mode to connect to and query an existing database using inspectdb.
PAOLO MELCHIORRE
Projects & Code
Events
Weekly Real Python Office Hours Q&A (Virtual)
February 25, 2026
REALPYTHON.COM
MLOps Open Source Sprint
February 27, 2026
MEETUP.COM
Melbourne Python Users Group, Australia
March 2, 2026
J.MP
PyBodensee Monthly Meetup
March 2, 2026
PYBODENSEE.COM
Python Unplugged on PyTV
March 4 to March 5, 2026
JETBRAINS.COM
Happy Pythoning!
This was PyCoder’s Weekly Issue #723.
View in Browser »
[ Subscribe to 🐍 PyCoder’s Weekly 💌 – Get the best Python news, articles, and tutorials delivered to your inbox once a week >> Click here to learn more ]
February 24, 2026 07:30 PM UTC
Real Python
Start Building With FastAPI
FastAPI is a web framework for building APIs with Python. It leverages standard Python type hints to provide automatic validation, serialization, and interactive documentation. When you’re deciding between Python web frameworks, FastAPI stands out for its speed, developer experience, and built-in features that reduce boilerplate code for API development:
| Use Case | Pick FastAPI | Pick Flask or Django |
|---|---|---|
| You want to build an API-driven web app | ✅ | — |
| You need a full-stack web framework | — | ✅ |
| You value automatic API documentation | ✅ | — |
Whether you’re building a minimal REST API or a complex backend service, understanding core features of FastAPI will help you make an informed decision about adopting it for your projects. To get the most from this video course, you’ll benefit from having basic knowledge of Python functions, HTTP concepts, and JSON handling.
[ Improve Your Python With 🐍 Python Tricks 💌 – Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. >> Click here to learn more and see examples ]
February 24, 2026 02:00 PM UTC
The Python Coding Stack
“Python’s Plumbing” Is Not As Flashy as “Magic Methods” • But Is It Better?
You’ve heard this phrase before: “Everything is an object in Python”. But here’s another phrase that’s related but rather less catchy:
Everything goes through special methods (dunder methods) in Python
Special methods are everywhere. However, you don’t see them. In fact, you’re not meant to use them directly unless you’re defining them within a class. They’re out of sight. But they keep everything moving smoothly in Python.
Here’s a short essay exploring where these special methods fit within Python.
Why Should I Care About Special Methods?
“Everything goes through special methods in Python.” I should probably preface the phrase with “almost”, but the phrase is already unwieldy as it is.
You want to display an object on the screen? Python looks for guidance in .__str__() or .__repr__().
You want to use the object in a for loop? Is it even possible? Python looks for .__iter__() to check whether it can iterate over the object and how.
Do you want to fetch an individual item from the object? If this makes sense for this object, then it will have a .__getitem__() special method.
How should Python interpret an object’s truthiness? There’s .__bool__() for that. Or .__len__()!
Ah, you’d like to add an object to another object. Does your object have a .__add__() special method?
I could go on. I’ll post links to articles that cover some of these special methods in more detail below.
I’m also running a two-hour workshop this Thursday, 26 February, called Python’s Plumbing • Dunder Methods and Python’s Hidden Interface
Many operations you take for granted in your code are governed by special methods. Each class defines the special methods it needs, and Python knows how to handle instances of that class through those methods.
But let’s talk about different ways we refer to these special methods.
What’s In A Name?
These methods are called special methods. That’s their official name. These special methods have double underscores at the beginning and end of their names, such as .__init__(), .__str__(), and .__iter__(). This double-underscore notation led to the informal name “dunder methods”. And let’s face it, most people call them “dunder methods” instead of their actual name: “special methods.”
I often call them dunder methods, too. However, the term dunder merely describes the syntax, double underscore, so it doesn’t tell us much about what they do. The term special doesn’t tell us what they do, either, but it shows us they have a special role in Python.
There’s No Such Thing as Magic
Some people also call them magic methods. However, I avoid this term, and I discourage students from using it. It makes these methods look unnecessarily mysterious, perhaps difficult to understand because it’s all down to magic.
But there’s no such thing as magic (unless you’re Harry Potter). And the magic tricks we see from real-world “magicians” are just that – tricks. The magic dissolves away once you know how the trick works.
And if you’re learning Python, then you need to learn how to be a magician. You need to learn the “magic tricks.” Therefore, they’re no longer magic!
Python’s Plumbing (”Plumbing Methods”, Anyone?)
So, “special method” tells us that these methods are important, but it doesn’t tell us what they do. “Dunder method” describes the syntax. “Magic method” misleads us and doesn’t provide any useful insight.
How about “plumbing methods” then? Now, before anyone takes me too seriously, I’m saying this with my tongue firmly in my cheek. I’m not that foolish to suggest a new term for the whole Python community to adopt. And it’s not as flashy as “magic methods” or as cool as “dunder methods”. But bear with me…
Let’s explore the analogy, even if the term won’t catch on.
Disclaimer: I know very little about plumbing. But I think that’s OK for this essay!
There are pipes, valves, and other stuff carrying water (clean or otherwise) around your house. You know they’re there. You need them there. But you don’t see them.
You don’t think about these pipes unless you’re building the house – or unless the pipes are blocked or leaking.
The house’s plumbing keeps things running smoothly. Yet, it’s out of sight, and you don’t normally think about it. You take it for granted.
You see where I’m going, right?
Python’s special methods perform the same role. You don’t normally see them when coding since they’re called implicitly, behind the scenes. You do need to define the special methods you need when you’re defining the class, just like you’ll need to lay the pipes when building or modifying your house.
And if something goes wrong in your code, you may need to dive into how these dunder methods behave, just as when you have a leak and need to explore which pipe is responsible.
Good plumbing is reliable, predictable. Bad plumbing is asking for trouble. The same applies to the infrastructure you create through the special methods you define in classes.
So, there you go, they’re “plumbing methods”. This name tells us what they do!
I’m running a two-hour live workshop this Thursday called Python’s Plumbing • Dunder Methods and Python’s Hidden Interface. This is your last chance to join and I may not run this workshop again for a while.
This workshop is the first of three in the Python Behind the Scenes series. The other two workshops in the series are:
#2 • Pythonic Iteration: Iterables, Iterators,
itertools#3 • To Inherit or Not? Inheritance, Composition, Abstract Base Classes, and Protocols
Join all three, or pick and choose:
Image by Pete Linforth from Pixabay
For more Python resources, you can also visit Real Python—you may even stumble on one of my own articles or courses there!
Also, are you interested in technical writing? You’d like to make your own writing more narrative, more engaging, more memorable? Have a look at Breaking the Rules.
And you can find out more about me at stephengruppetta.com
Further reading related to this article’s topic:
This is part of a longer OOP series: Time for Something Special • Special Methods in Python Classes
The Manor House, the Oak-Panelled Library, the Vending Machine, and Python’s __getitem__() [Part 1]
Why Do 5 + “5” and “5” + 5 Give Different Errors in Python? • Do You Know The Whole Story?
February 24, 2026 01:56 PM UTC
PyBites
Why do we insist on struggling alone?
A realisation about my son’s basketball team reminded me that we should never be ashamed to ask for help, or better yet, seek formal coaching/support.
Last year, for two straight seasons, my son’s team got absolutely smashed on the court.
They had the energy and the determination, but they were effectively running in circles without any real guidance (and I’m definitely not a basketball player!).
Sound familiar? It should!
It’s exactly what it feels like when you can’t figure out where you’re going wrong, stuck in tutorial hell or banging your head against a wall trying to architect an application by yourself.
You end up spending hours debugging something a senior developer could easily point out in a 5-minute PR review. To put it another way – you’re wasting the most valuable resource you have: your time.
Everything changed for my son’s team when we brought in an experienced coach to help. He analysed their play style, identified each of their strengths and gaps, then gave them proven, concrete steps to correct their form. They just finished their latest season in first place.
This is the exact strategy behind the Pybites Developer Mindset (PDM) program. PDM is a 12-week personalised 1:1 coaching program focused on project-based development, designed to bridge specific gaps in an individual’s knowledge. This is bespoke coaching to help you where you need it.
We provide detailed, actionable PR reviews to speed up the learning process. You’ll learn to navigate real-world constraints that go beyond your code, like hosting, deployment and stakeholder needs.
Stop guessing and start building with a mentor who will reinforce professional developer skills and validate your technical direction.
You can use the links below to chat with us about how we can best help. There really is no need to go it alone!
Julian
This was originally sent to our email list. Join here.
And if you do decide to go alone…

February 24, 2026 03:36 AM UTC
Seth Michael Larson
Respecting maintainer time should be in security policies
Generative AI tools becoming more common means that vulnerability reports these days are loooong. If you're an open source maintainer, you unfortunately know what I'm talking about. Markdown-formatted, more than five headings, similar in length to a blog post, and characterized as a vulnerability worthy of its own domain name.
This makes triaging vulnerabilities by often under-resourced maintainer more difficult, time-consuming, and stressful. Whether a report is a genuine vulnerability or not, it now requires more time from maintainers to make a determination than is necessary. I've heard from multiple maintainers how specifically report length weighs negatively on maintainer time, whether these are “slop vulnerability reports” or just overly-thorough reporters.
David Lord, the maintainer of Flask and Pallets, captures this problem concisely, that the best security reports respect maintainer time:
Post by @davidism@mas.toView on Mastodon
Here's my proposal: require security reports respect maintainer time in your security policy. This especially applies to “initial” security reports, where the reporter is most likely to send disproportionately more information than is needed to make an initial determination.
The best part about this framing is you don't have to mention the elephant in the room. Here's a few example security policy requirements to include:
- Initial reports must be six or fewer sentences describing the issue and optionally a short proof-of-concept script. Follow-ups may be longer if the initial report is deemed a vulnerability.
- Initial reports must not contain a severity (such as: "critical") or CVSS score. This calculation will be completed after the report is accepted by maintainers.
- Reports must not make a determination whether a behavior of the software represents a vulnerability.
Notice I didn't even have to mention LLMs or generative AI, so there’s no ambiguity about whether a given report follows the policy or not. While you have reporters reading your security policy, you might also add suggestions that also benefit maintainers remediating vulnerabilities faster:
- If applicable, submitting a patch or an expected behavior along with a proof-of-concept makes remediating a vulnerability easier.
- We appreciate vulnerability reporters that are willing to review patches prior to publication.
- If you would like to be credited as a reporter, please mention that in your report.
After this is added to a project security policy (preferably under its own linkable heading) then any security report that doesn't respect maintainer time can be punted back to the reporter with a canned response:
Your report doesn't meet our security policy: https://... Please amend your report to meet our policy so we may efficiently make a determination and remediation. Thank you!
Now your expectations have been made clear to reporters and valuable maintainer time is saved. From here the security report can evolve more like a dialogue which requires maintainer time and energy proportionate to the value that the report represents to the project.
I understand this runs counter to how many vulnerability teams work today. Many reporters opt to provide as much context and detail up-front in a single report, likely to reduce back-and-forth or push-back from projects. If teams reporting vulnerabilities to open source projects want to be the most effective, they should meet the pace and style that best suites the project they are reporting to.
Please note that many vulnerability reporters are acting in good faith and aren't trying to burden maintainers. If you believe your peer is acting in good faith, maybe give them a pass if the report doesn't strictly meet the requirements and save the canned response for the bigger offenders.
Have any thoughts about this topic? Have you seen this in any open source security policies already? Let me know! Thanks to OSTIF founder Derek Zimmer for reviewing this blog post prior to publication.
Thanks for keeping RSS alive! ♥
February 24, 2026 12:00 AM UTC
Python⇒Speed
Unit testing your code's performance, part 2: Catching speed changes
In a previous post I talked about unit testing for speed, and in particular testing for big-O scalability. The next step is catching cases where you’ve changed not the scalability, but the direct efficiency of your code.
If your first thought is “how this is different from running benchmarks?”, well, good point! An excellent starting point for performance is implementing a benchmark that runs automatically in CI, on every single pull request. If you haven’t got that, you probably want to go do that first.
Once you have implemented CI benchmarks, they will typically run when you submit a pull request or the equivalent. And if you’re doing performance work, that’s hopefully just a formality, as you likely have been benchmarking your code locally as you work.
But what happens when you or a colleague are working on features or bugfixes, and accidentally modify a performance-critical code path? You make changes, run the tests locally, run a linter, open a pull request… and now the benchmark runs, and tells you that your code has made things slower. This is annoying, because now you have to go back and figure out which specific change was the cause.
So what you really want is to get some sense of whether performance changed much earlier in the process, giving you immediate feedback when you’re running tests locally. Since a reliable benchmark environment is hard, switching to a test might allow for an early warning.
Read more...February 24, 2026 12:00 AM UTC
Israel Fruchter
Coodie: A 4-year-old idea brought to life by AI (and some coffee)
So, let’s rewind a bit. About four years ago, I was looking at Beanie — this really nifty, Pydantic-based ODM for MongoDB. And as someone who spends an unhealthy amount of time deep in the trenches of ScyllaDB and Cassandra, I had a thought: “Where is my Beanie? I want a hoodie, but for Cassandra.” And thus, the name was born: coodie = cassandra + beanie (hoodie). Catchy, right?
Like any respectable developer, I rushed to GitHub, created the repository fruch/coodie, maybe wrote a highly ambitious README.md, set up a pyproject.toml, and then… absolutely nothing. Crickets. Life happened. I had CI pipelines to fix, Scylla drivers to maintain, conferences like PyConIL and EuroPython to attend, and live-tweeting to do. coodie just sat there, gathering digital dust, a glorious monument to my good intentions and severe lack of free time.
Fast forward to today. The AI era.
We are living in a weird timeline where LLMs are everywhere, threatening to take our jobs while simultaneously failing to center a div. People are talking about AI coding assistants non-stop. I myself was quite happy with my usual workflow, but I figured — why not take my 4-year-old fever dream for a walk in the park and feed it to the machine?
I threw the basic concept at an AI. I gave it some ground rules: it has to use Pydantic v2, it needs to be backed by scylla-driver, and it needs to feel as magical as Beanie.
And holy crap. It actually worked.
I spent four years procrastinating on this, and a glorified autocomplete bot basically bootstrapped the whole thing while I was sipping my morning coffee. I’m not sure if I should be proud of my newfound status as a “prompt engineer,” or slightly terrified that my open-source street cred is now partially owned by a matrix of weights and biases.
The sweet setup we have now
Despite the AI doing the heavy lifting, the architecture actually makes a lot of sense. Here is what coodie brings to the table:
- Pydantic v2 all the way: Define your documents with full type-checking support.
- Declarative schemas: You just annotate fields with
PrimaryKey,ClusteringKey,Indexed, orCounter. - Automatic table management: You call
sync_table()and it creates or evolves the table idempotently. No more writing raw CQL just to add a column. - Sync and Async APIs: Because why choose? You can use
coodie.aioif you are riding the asyncio train, orcoodie.syncif you want blocking code. - Chainable QuerySets: Doing
await Product.find(brand="Acme").limit(10).all()just feels right.
Here is a quick taste of what the AI and I managed to cook up:
from typing import Annotated
from uuid import UUID, uuid4
from pydantic import Field
from coodie import Document, init_coodie, PrimaryKey
class Product(Document):
id: Annotated[UUID, PrimaryKey()] = Field(default_factory=uuid4)
name: str
price: float = 0.0
class Settings:
keyspace = "my_ks"
And then querying it is a breeze:
# async
products = (
await Product.find()
.filter(brand="Acme")
.order_by("price")
.limit(20)
.all()
)
Wrapping up
The AI works out of the box with almost zero friction. It’s very impressive, and honestly, a bit surreal to see an idea you abandoned years ago suddenly have a passing CI suite, complete with tests and GitHub Actions (which are still very tidy to look at, by the way).
You can check out the code, star it, or fork it over at github.com/fruch/coodie.
PRs are welcome. Preferably written by humans, but honestly… I guess I can’t really enforce that anymore, can I? יאללה, let’s see how it goes.
February 24, 2026 12:00 AM UTC
February 23, 2026
Anarcat
PSA: North america changes time forward soon, Europe next
This is a copy of an email I used to send internally at work and now made public. I'm not sure I'll make a habit of posting it here, especially not twice a year, unless people really like it. Right now, it's mostly here to keep with my current writing spree going.
This is your bi-yearly reminder that time is changing soon!
What's happening?
For people not on tor-internal, you should know that I've been sending semi-regular announcements when daylight saving changes occur. Starting now, I'm making those announcements public so they can be shared with the wider community because, after all, this affects everyone (kind of).
For those of you lucky enough to have no idea what I'm talking about, you should know that some places in the world implement what is called Daylight saving time or DST.
Normally, you shouldn't have to do anything: computers automatically change time following local rules, assuming they are correctly configured, provided recent updates have been applied in the case of a recent change in said rules (because yes, this happens).
Appliances, of course, will likely not change time and will need to adjusted unless they are so-called "smart" (also known as "part of a bot net").
If your clock is flashing "0:00" or "12:00", you have no action to take, congratulations on having the right time once or twice a day.
If you haven't changed those clocks in six months, congratulations, they will be accurate again!
In any case, you should still consider DST because it might affect some of your meeting schedules, particularly if you set up a new meeting schedule in the last 6 months and forgot to consider this change.
If your location does not have DST
Properly scheduled meetings affecting multiple time zones are set in UTC time, which does not change. So if your location does not observer time changes, your (local!) meeting time will not change.
But be aware that some other folks attending your meeting might have the DST bug and their meeting times will change. They might miss entire meetings or arrive late as you frantically ping them over IRC, Matrix, Signal, SMS, Ricochet, Mattermost, SimpleX, Whatsapp, Discord, Slack, Wechat, Snapchat, Telegram, XMPP, Briar, Zulip, RocketChat, DeltaChat, talk(1), write(1), actual telegrams, Meshtastic, Meshcore, Reticulum, APRS, snail mail, and, finally, flying a remote presence drone to their house, asking what's going on.
(Sorry if I forgot your preferred messaging client here, I tried my best.)
Be kind; those poor folks might be more sleep deprived as DST steals one hour of sleep from them on the night that implements the change.
If you do observe DST
If you are affected by the DST bug, your local meeting times will change access the board. Normally, you can trust that your meetings are scheduled to take this change into account and the new time should still be reasonable.
Trust, but verify; make sure the new times are adequate and there are no scheduling conflicts.
Do this now: take a look at your calendar in two week and in April. See if any meeting need to be rescheduled because of an impossible or conflicting time.
When does time change, how and where?
Notice how I mentioned "North America" in the subject? That's a lie. ("The doctor lies", as they say on the BBC.) Other places, including Europe, also changes times, just not all at once (and not all North America).
We'll get into "where" soon, but first let's look at the "how". As you might already know, the trick is:
Spring forward, fall backwards.
This northern-centric (sorry!) proverb says that clocks will move forward by an hour this "spring", after moving backwards last "fall". This is why we lose an hour of work, sorry, sleep. It sucks, to put it bluntly. I want it to stop and will keep writing those advisories until it does.
To see where and when, we, unfortunately, still need to go into politics.
USA and Canada
First, we start with "North America" which, really, is just some parts of USA[1] and Canada[2]. As usual, on the Second Sunday in March (the 8th) at 02:00 local (not UTC!), the clocks will move forward.
This means that properly set clocks will flip from 1:59 to 3:00, coldly depriving us from an hour of sleep that was perniciously granted 6 months ago and making calendar software stupidly hard to write.
Practically, set your wrist watch and alarm clocks[3] back one hour before going to bed and go to bed early.
[1] except Arizona (except the Navajo nation), US territories, and Hawaii
[2] except Yukon, most of Saskatchewan, and parts of British Columbia (northeast), one island in Nunavut (Southampton Island), one town in Ontario (Atikokan) and small parts of Quebec (Le Golfe-du-Saint-Laurent), a list which I keep recopying because I find it just so amazing how chaotic it is. When your clock has its own Wikipedia page, you know something is wrong.
[3] hopefully not managed by a botnet, otherwise kindly ask your bot net operator to apply proper software upgrades in a timely manner
Europe
Next we look at our dear Europe, which will change time on the last Sunday in March (the 29th) at 01:00 UTC (not local!). I think it means that, Amsterdam-time, the clocks will flip from 1:59 to 3:00 AM local on that night.
(Every time I write this, I have doubts. I would welcome independent confirmation from night owls that observe that funky behavior experimentally.)
Just like your poor fellows out west, just fix your old-school clocks before going to bed, and go to sleep early, it's good for you.
Rest of the world with DST
Renewed and recurring apologies again to the people of Cuba, Mexico, Moldova, Israel, Lebanon, Palestine, Egypt, Chile (except Magallanes Region), parts of Australia, and New Zealand which all have their own individual DST rules, omitted here for brevity.
In general, changes also happen in March, but either on different times or different days, except in the south hemisphere, where they happen in April.
Rest of the world without DST
All of you other folks without DST, rejoice! Thank you for reminding us how manage calendars and clocks normally. Sometimes, doing nothing is precisely the right thing to do. You're an inspiration for us all.
Changes since last time
There were, again, no changes since last year on daylight savings that I'm aware of. It seems the US congress debating switching to a "half-daylight" time zone which is an half-baked idea that I should have expected from the current USA politics.
The plan is to, say, switch from "Eastern is UTC-4 in the summer" to "Eastern is UTC-4.5". The bill also proposes to do this 90 days after enactment, which is dangerously optimistic about our capacity at deploying any significant change in human society.
In general, I rely on the Wikipedia time nerds for this and Paul Eggert which seems to singlehandledly be keeping everything in order for all of us, on the tz-announce mailing list.
This time, I've also looked at the tz mailing list which is where I learned about the congress bill.
If your country has changed time and no one above noticed, now would be an extremely late time to do something about this, typically writing to the above list. (Incredibly, I need to write to the list because of this post.)
One thing that did change since last year is that I've implemented what I hope to be a robust calendar for this, which was surprisingly tricky.
If you have access to our Nextcloud, it should be visible under the heading "Daylight saving times". If you don't, you can access it using this direct link.
The procedures around how this calendar was created, how this email was written, and curses found along the way, are also documented in this wiki page, if someone ever needs to pick up the Time Lord duty.
February 23, 2026 07:31 PM UTC
Real Python
Python for Loops: The Pythonic Way
Python’s for loop allows you to iterate over the items in a collection, such as lists, tuples, strings, and dictionaries. The for loop syntax declares a loop variable that takes each item from the collection in each iteration. This loop is ideal for repeatedly executing a block of code on each item in the collection. You can also tweak for loops further with features like break, continue, and else.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll understand that:
- Python’s
forloop iterates over items in a data collection, allowing you to execute code for each item. - To iterate from
0to10, you use thefor index in range(11):construct. - To repeat code a number of times without processing the data of an iterable, use the
for _ in range(times):construct. - To do index-based iteration, you can use
for index, value in enumerate(iterable):to access both index and item.
In this tutorial, you’ll gain practical knowledge of using for loops to traverse various collections and learn Pythonic looping techniques. You’ll also learn how to handle exceptions and use asynchronous iterations to make your Python code more robust and efficient.
Get Your Code: Click here to download the free sample code that shows you how to use for loops in Python.
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python for Loops: The Pythonic Way” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Python for Loops: The Pythonic WayIn this quiz, you'll test your understanding of Python's for loop. You'll revisit how to iterate over items in a data collection, how to use range() for a predefined number of iterations, and how to use enumerate() for index-based iteration.
Getting Started With the Python for Loop
In programming, loops are control flow statements that allow you to repeat a given set of operations a number of times. In practice, you’ll find two main types of loops:
forloops are mostly used to iterate a known number of times, which is common when you’re processing data collections with a specific number of data items.whileloops are commonly used to iterate an unknown number of times, which is useful when the number of iterations depends on a given condition.
Python has both of these loops and in this tutorial, you’ll learn about for loops. In Python, you’ll generally use for loops when you need to iterate over the items in a data collection. This type of loop lets you traverse different data collections and run a specific group of statements on or with each item in the input collection.
In Python, for loops are compound statements with a header and a code block that runs a predefined number of times. The basic syntax of a for loop is shown below:
for variable in iterable:
<body>
In this syntax, variable is the loop variable. In each iteration, this variable takes the value of the current item in iterable, which represents the data collection you need to iterate over. The loop body can consist of one or more statements that must be indented properly.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of this syntax:
foris the keyword that initiates the loop header.variableis a variable that holds the current item in the input iterable.inis a keyword that connects the loop variable with the iterable.iterableis a data collection that can be iterated over.<body>consists of one or more statements to execute in each iteration.
Here’s a quick example of how you can use a for loop to iterate over a list:
>>> colors = ["red", "green", "blue", "yellow"]
>>> for color in colors:
... print(color)
...
red
green
blue
yellow
In this example, color is the loop variable, while the colors list is the target collection. Each time through the loop, color takes on a successive item from colors. In this loop, the body consists of a call to print() that displays the value on the screen. This loop runs once for each item in the target iterable. The way the code above is written is the Pythonic way to write it.
However, what’s an iterable anyway? In Python, an iterable is an object—often a data collection—that can be iterated over. Common examples of iterables in Python include lists, tuples, strings, dictionaries, and sets, which are all built-in data types. You can also have custom classes that support iteration.
Note: Python has both iterables and iterators. Iterables support the iterable protocol consisting of the .__iter__() special method. Similarly, iterators support the iterator protocol that’s based on the .__iter__() and .__next__() special methods.
Both iterables and iterators can be iterated over. All iterators are iterables, but not all iterables are iterators. Python iterators play a fundamental role in for loops because they drive the iteration process.
A deeper discussion on iterables and iterators is beyond the scope of this tutorial. However, to learn more about them, check out the Iterators and Iterables in Python: Run Efficient Iterations tutorial.
You can also have a loop with multiple loop variables:
>>> points = [(1, 4), (3, 6), (7, 3)]
>>> for x, y in points:
... print(f"{x = } and {y = }")
...
x = 1 and y = 4
x = 3 and y = 6
x = 7 and y = 3
In this loop, you have two loop variables, x and y. Note that to use this syntax, you just need to provide a tuple of loop variables. Also, you can have as many loop variables as you need as long as you have the correct number of items to unpack into them. You’ll also find this pattern useful when iterating over dictionary items or when you need to do parallel iteration.
Sometimes, the input iterable may be empty. In that case, the loop will run its header once but won’t execute its body:
>>> for item in []:
... print(item)
...
Read the full article at https://realpython.com/python-for-loop/ »
[ Improve Your Python With 🐍 Python Tricks 💌 – Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. >> Click here to learn more and see examples ]
February 23, 2026 02:00 PM UTC
Quiz: Build a Hash Table in Python With TDD
In this quiz, you’ll review hash functions, collision resolution strategies, hash function distribution, the avalanche effect, and key principles of Test-Driven Development.
For more practice and context, explore Build a Hash Table in Python With TDD.
[ Improve Your Python With 🐍 Python Tricks 💌 – Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. >> Click here to learn more and see examples ]
February 23, 2026 12:00 PM UTC
Python Bytes
#470 A Jolting Episode
<strong>Topics covered in this episode:</strong><br> <ul> <li><strong><a href="https://pydantic.dev/articles/inline-snapshot?featured_on=pythonbytes">Better Python tests with inline-snapshot</a></strong></li> <li><strong><a href="https://getjolt.sh/?featured_on=pythonbytes">jolt Battery intelligence for your laptop</a></strong></li> <li><strong><a href="https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/formatter/#markdown-code-formatting">Markdown code formatting with ruff</a></strong></li> <li><strong><a href="https://github.com/nektos/act?featured_on=pythonbytes">act - run your GitHub actions locally</a></strong></li> <li><strong>Extras</strong></li> <li><strong>Joke</strong></li> </ul><a href='https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MT2zsZ-lGzg' style='font-weight: bold;'data-umami-event="Livestream-Past" data-umami-event-episode="470">Watch on YouTube</a><br> <p><strong>About the show</strong></p> <p>Sponsored by us! Support our work through:</p> <ul> <li>Our <a href="https://training.talkpython.fm/?featured_on=pythonbytes"><strong>courses at Talk Python Training</strong></a></li> <li><a href="https://courses.pythontest.com/p/the-complete-pytest-course?featured_on=pythonbytes"><strong>The Complete pytest Course</strong></a></li> <li><a href="https://www.patreon.com/pythonbytes"><strong>Patreon Supporters</strong></a> <strong>Connect with the hosts</strong></li> <li>Michael: <a href="https://fosstodon.org/@mkennedy">@mkennedy@fosstodon.org</a> / <a href="https://bsky.app/profile/mkennedy.codes?featured_on=pythonbytes">@mkennedy.codes</a> (bsky)</li> <li>Brian: <a href="https://fosstodon.org/@brianokken">@brianokken@fosstodon.org</a> / <a href="https://bsky.app/profile/brianokken.bsky.social?featured_on=pythonbytes">@brianokken.bsky.social</a></li> <li>Show: <a href="https://fosstodon.org/@pythonbytes">@pythonbytes@fosstodon.org</a> / <a href="https://bsky.app/profile/pythonbytes.fm">@pythonbytes.fm</a> (bsky) Join us on YouTube at <a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/stream/live"><strong>pythonbytes.fm/live</strong></a> to be part of the audience. Usually <strong>Monday</strong> at 11am PT. Older video versions available there too. Finally, if you want an artisanal, hand-crafted digest of every week of the show notes in email form? Add your name and email to <a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/friends-of-the-show">our friends of the show list</a>, we'll never share it.</li> </ul> <p><strong>Brian #1: <a href="https://pydantic.dev/articles/inline-snapshot?featured_on=pythonbytes">Better Python tests with inline-snapshot</a></strong></p> <ul> <li>Alex Hall, on Pydantic blog</li> <li>Great for testing complex data structures</li> <li><p>Allows you to write a test like this:</p> <div class="codehilite"> <pre><span></span><code><span class="n">from</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">inline_snapshot</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">import</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">snapshot</span> <span class="n">def</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">test_user_creation</span><span class="err">():</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="n">user</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="o">=</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="err">create</span><span class="mi">_</span><span class="n">user</span><span class="err">(</span><span class="n">id</span><span class="o">=</span><span class="mi">123</span><span class="err">,</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">name</span><span class="o">=</span><span class="s2">"test_user"</span><span class="err">)</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="n">assert</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">user</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="n">dict</span><span class="err">()</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="o">=</span><span class="err">= snapshot(</span><span class="p">{}</span><span class="err">)</span> </code></pre> </div></li> <li><p>Then run <code>pytest --inline-snapshot=fix</code></p></li> <li><p>And the library updates the test source code to look like this:</p> <div class="codehilite"> <pre><span></span><code><span class="n">def</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">test_user_creation</span><span class="err">():</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="n">user</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="o">=</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="err">create</span><span class="mi">_</span><span class="n">user</span><span class="err">(</span><span class="n">id</span><span class="o">=</span><span class="mi">123</span><span class="err">,</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">name</span><span class="o">=</span><span class="s2">"test_user"</span><span class="err">)</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="n">assert</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">user</span><span class="p">.</span><span class="n">dict</span><span class="err">()</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="o">=</span><span class="err">= snapshot(</span><span class="p">{</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="s2">"id"</span><span class="err">:</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="n">123</span><span class="err">,</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="s2">"name"</span><span class="err">:</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="s2">"test_user"</span><span class="err">,</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="s2">"status"</span><span class="err">:</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="s2">"active"</span> <span class="w"> </span><span class="err">})</span> </code></pre> </div></li> <li><p>Now, when you run the code without “fix” the collected data is used for comparison</p></li> <li>Awesome to be able to visually inspect the test data right there in the test code.</li> <li>Projects mentioned <ul> <li><a href="https://15r10nk.github.io/inline-snapshot/latest/?featured_on=pythonbytes">inline-snapshot</a></li> <li><a href="https://github.com/pydantic/pytest-examples?featured_on=pythonbytes">pytest-examples</a></li> <li><a href="https://github.com/syrupy-project/syrupy?featured_on=pythonbytes">syrupy</a></li> <li><a href="https://github.com/samuelcolvin/dirty-equals?featured_on=pythonbytes">dirty-equals</a></li> <li><a href="https://github.com/alexmojaki/executing?featured_on=pythonbytes">executing</a></li> </ul></li> </ul> <p><strong>Michael #2: <a href="https://getjolt.sh/?featured_on=pythonbytes">jolt Battery intelligence for your laptop</a></strong></p> <ul> <li>Support for both macOS and Linux</li> <li><strong>Battery Status</strong> — Charge percentage, time remaining, health, and cycle count</li> <li><strong>Power Monitoring</strong> — System power draw with CPU/GPU breakdown</li> <li><strong>Process Tracking</strong> — Processes sorted by energy impact with color-coded severity</li> <li><strong>Historical Graphs</strong> — Track battery and power trends over time</li> <li><strong>Themes</strong> — 10+ built-in themes with dark/light auto-detection</li> <li><strong>Background Daemon</strong> — Collect historical data even when the TUI isn't running</li> <li><strong>Process Management</strong> — Kill energy-hungry processes directly</li> </ul> <p><strong>Brian #3: <a href="https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/formatter/#markdown-code-formatting">Markdown code formatting with ruff</a></strong></p> <ul> <li>Suggested by Matthias Schoettle</li> <li><code>ruff</code> can now format code within markdown files</li> <li>Will format valid Python code in code blocks marked with <code>python</code>, <code>py</code>, <code>python3</code> or <code>py3</code>.</li> <li>Also recognizes <code>pyi</code> as Python type stub files.</li> <li>Includes the ability to turn off formatting with comment <code>[HTML_REMOVED]</code> , <code>[HTML_REMOVED]</code> blocks.</li> <li>Requires preview mode <div class="codehilite"> <pre><span></span><code><span class="k">[tool.ruff.lint]</span> <span class="n">preview</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="o">=</span><span class="w"> </span><span class="kc">true</span> </code></pre> </div></li> </ul> <p><strong>Michael #4: <a href="https://github.com/nektos/act?featured_on=pythonbytes">act - run your GitHub actions locally</a></strong></p> <ul> <li>Run your <a href="https://developer.github.com/actions/?featured_on=pythonbytes">GitHub Actions</a> locally! Why would you want to do this? Two reasons: <ul> <li><strong>Fast Feedback</strong> - Rather than having to commit/push every time you want to test out the changes you are making to your <code>.github/workflows/</code> files (or for any changes to embedded GitHub actions), you can use <code>act</code> to run the actions locally. The <a href="https://help.github.com/en/actions/configuring-and-managing-workflows/using-environment-variables#default-environment-variables">environment variables</a> and <a href="https://help.github.com/en/actions/reference/virtual-environments-for-github-hosted-runners#filesystems-on-github-hosted-runners">filesystem</a> are all configured to match what GitHub provides.</li> <li><strong>Local Task Runner</strong> - I love <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Make_(software)?featured_on=pythonbytes">make</a>. However, I also hate repeating myself. With <code>act</code>, you can use the GitHub Actions defined in your <code>.github/workflows/</code> to replace your <code>Makefile</code>!</li> </ul></li> <li>When you run <code>act</code> it reads in your GitHub Actions from <code>.github/workflows/</code> and determines the set of actions that need to be run. <ul> <li>Uses the Docker API to either pull or build the necessary images, as defined in your workflow files and finally determines the execution path based on the dependencies that were defined.</li> <li>Once it has the execution path, it then uses the Docker API to run containers for each action based on the images prepared earlier.</li> <li>The <a href="https://help.github.com/en/actions/configuring-and-managing-workflows/using-environment-variables#default-environment-variables">environment variables</a> and <a href="https://docs.github.com/en/actions/using-github-hosted-runners/about-github-hosted-runners#file-systems">filesystem</a> are all configured to match what GitHub provides.</li> </ul></li> </ul> <p><strong>Extras</strong></p> <p>Michael:</p> <ul> <li>Winter is coming: <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7427589361048948736/?utm_source=share&utm_medium=member_desktop&rcm=ACoAAABOjqABPkOWTTbZXV9tmnQohvpkplQOibU&featured_on=pythonbytes">Frozendict accepted</a></li> <li><a href="https://mastodon.social/@webology/116103649163718377?featured_on=pythonbytes">Django ORM stand-alone</a></li> <li>Command Book app <a href="https://mkennedy.codes/posts/your-terminal-tabs-are-fragile-i-built-something-better/?featured_on=pythonbytes">announcement post</a></li> </ul> <p><strong>Joke:</strong> <a href="https://x.com/pr0grammerhum0r/status/2017704478267314514?s=12&featured_on=pythonbytes">Plug ‘n Paste</a></p>
February 23, 2026 08:00 AM UTC
Tibo Beijen
Introducing the Zen of DevOps
Introduction Over the past ten years or so, my role has gradually shifted from software to platforms. More towards the ‘ops’ side of things, but coming from a background that values APIs, automation, artifacts and guardrails in the form of automated tests. And I found out that a lot of best practices from software engineering can be adapted and applied to modern ops practices as well. DevOps in a nutshell really: Bridging the gap between Dev and Ops.
February 23, 2026 04:00 AM UTC
February 22, 2026
Graham Dumpleton
Teaching an AI about Educates
The way we direct AI coding agents has changed significantly over the past couple of years. Early on, the interaction was purely conversational. You'd open a chat, explain what you wanted, provide whatever context seemed relevant, and hope the model could work with it. If it got something wrong or went down the wrong path, you'd correct it and try again. It worked, but it was ad hoc. Every session started from scratch. Every conversation required re-establishing context.
What's happened since then is a steady progression toward giving agents more structured, persistent knowledge to work with. Each step in that progression has made agents meaningfully more capable, to the point where they can now handle tasks that would have been unrealistic even a year ago. I've been putting these capabilities to work on a specific challenge: getting an AI to author interactive workshops for the Educates training platform. In my previous posts I talked about why workshop content is actually a good fit for AI generation. Here I want to explain how I've been making that work in practice.
How agent steering has evolved
The first real step beyond raw prompting was agent steering files. These are files you place in a project directory that give the agent standing instructions whenever it works in that context. Think of it as a persistent briefing document. You describe the project structure, the conventions to follow, the tools to use, and the agent picks that up automatically each time you interact with it. No need to re-explain the basics of your codebase every session. This was a genuine improvement, but the instructions are necessarily general-purpose. They tell the agent about the project, not about any particular domain of expertise.
The next step was giving agents access to external tools and data sources through protocols like the Model Context Protocol (MCP). Instead of the agent only being able to read and write files, it could now make API calls, query databases, fetch documentation, and interact with external services. The agent went from being a conversationalist that could edit code to something that could actually do things in the world. That opened up a lot of possibilities, but the agent still needed you to explain what to do and how to approach it.
Planning modes added another layer. Rather than the agent diving straight into implementation, it could first think through the approach, break a complex task into steps, and present a plan for review before acting. This was especially valuable for larger tasks where getting the overall approach right matters more than any individual step. The agent became more deliberate and less likely to charge off in the wrong direction.
Skills represent where things stand now, and they're the piece that ties the rest together. A skill is a self-contained package of domain knowledge, workflow guidance, and reference material that an agent can invoke when working on a specific type of task. Rather than the agent relying solely on what it learned during training, a skill gives it authoritative, up-to-date, structured knowledge about a particular domain. The agent knows when to use the skill, what workflow to follow, and which reference material to consult for specific questions.
With the advances in what LLMs are capable of combined with these structured ways of steering them, agents are genuinely reaching a point where their usefulness is growing in ways that matter for real work.
Why model knowledge isn't enough
Large language models know something about most topics. If you ask an AI about Educates, it will probably have some general awareness of the project. But general awareness is not the same as the detailed, precise knowledge you need to produce correct output for a specialised platform.
Educates workshops have specific YAML structures for their configuration files. The interactive instructions use a system of clickable actions with particular syntax for each action type. There are conventions around how learners interact with terminals and editors, how dashboard tabs are managed, how Kubernetes resources are configured, and how data variables are used for parameterisation. Getting any of these wrong doesn't just produce suboptimal content, it produces content that simply won't work when someone tries to use it.
I covered the clickable actions system in detail in my last post. There are eight categories of actions covering terminal execution, file viewing and editing, YAML-aware modifications, validation, and more. Each has its own syntax and conventions. An AI that generates workshop content needs to use all of these correctly, not approximately, not most of the time, but reliably.
This is where skills make the difference. Rather than hoping the model has absorbed enough Educates documentation during its training to get these details right, you give it the specific knowledge it needs. The skill becomes the agent's reference manual for the domain, structured in a way that supports the workflow rather than dumping everything into context at once.
The Educates workshop authoring skill
The obvious approach would be to take the full Educates documentation and load it into the agent's context. But AI agents work within a finite context window, and that window is shared between the knowledge you give the agent and the working space it needs for the actual task. Generating a workshop involves reasoning about structure, producing instruction pages, writing clickable action syntax, and keeping track of what's been created so far. If you consume most of the context with raw documentation, there's not enough room left for the agent to do its real work. You have to be strategic about what goes in.
The skill I built for Educates workshop authoring is a deliberate distillation. At its core is a main skill definition of around 25 kilobytes that captures the essential workflow an agent follows when creating a workshop. It covers gathering requirements from the user, creating the directory structure, generating the workshop configuration file, writing instruction pages with clickable actions, and running through verification checklists at the end. This isn't a copy of the documentation. It's the key knowledge extracted and organised to drive the workflow correctly.
Supporting that are 20+ reference files totalling around 300 kilobytes. These cover specific aspects of the platform in the detail needed to get things right: the complete clickable actions system across all eight action categories, Kubernetes access patterns and namespace isolation, data variables for parameterising workshop content, language-specific references for Python and Java workshops, dashboard configuration and tab management, workshop image selection, setup scripts, and more.
The skill is organised around the workflow rather than being a flat dump of information. The main definition tells the agent what to do at each step, and the reference files are there for it to consult when it needs detail on a particular topic. If it's generating a terminal action, it knows to check the terminal actions reference for the correct syntax. If it's setting up Kubernetes access, it consults the Kubernetes reference for namespace configuration patterns. The agent pulls in the knowledge it needs when it needs it, keeping the active context focused on the task at hand.
There's also a companion skill for course design that handles the higher-level task of planning multi-workshop courses, breaking topics into individual workshops, and creating detailed plans for each one. But the workshop authoring skill is where the actual content generation happens, and it's the one I want to demonstrate.
Putting it to the test with Air
To show what the skill can do, I decided to use it to generate a workshop for the Air web framework. Air is a Python web framework written by friends in the Python community. It's built on FastAPI, Starlette, and HTMX, with a focus on simplicity and minimal JavaScript. What caught my attention about it as a test case is the claim on their website: "The first web framework designed for AI to write. Every framework claims AI compatibility. Air was architected for it." That's a bold statement, and using Air as the subject for this exercise is partly a way to see how that claim holds up in practice, not just for writing applications with the framework but for creating training material about it.
There's another reason Air makes for a good test. I haven't used the framework myself. I know the people behind it, but I haven't built anything with it. That means I can't fall back on my own knowledge to fill in gaps. The AI needs to research the framework and understand it well enough to teach it to someone, while the skill provides all the Educates platform knowledge needed to structure that understanding into a proper interactive workshop. It's a genuine test of both the skill and the model working together.
The process starts simply enough. You tell the agent what you want: create me a workshop for the Educates training platform introducing the Air web framework for Python developers. The phrasing matters here. The agent needs enough context in the request to recognise that a relevant skill exists and should be applied. Mentioning Educates in the prompt is what triggers the connection to the workshop authoring skill. Some agents also support invoking a skill directly through a slash command, which removes the ambiguity entirely. Either way, once the skill is activated, its workflow kicks in. It asks clarifying questions about the workshop requirements. Does it need an editor? (Yes, learners will be writing code.) Kubernetes access? (No, this is a web framework workshop, not a Kubernetes one.) What's the target difficulty and duration?
I'd recommend using the agent's planning mode for this initial step if it supports one. Rather than having the agent jump straight into generating files, planning mode lets it first describe what it intends to put in the workshop: the topics it will cover, the page structure, and the learning progression. You can review that plan and steer it before any files are created. It's a much better starting point than generating everything and then discovering the agent went in a direction you didn't want.
From those answers and the approved plan, it builds up the workshop configuration and starts generating content.
lab-python-air-intro/
├── CLAUDE.md
├── README.md
├── exercises/
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── pyproject.toml
│ └── app.py
├── resources/
│ └── workshop.yaml
└── workshop/
├── setup.d/
│ └── 01-install-packages.sh
├── profile
└── content/
├── 00-workshop-overview.md
├── 01-first-air-app.md
├── 02-air-tags.md
├── 03-adding-routes.md
└── 99-workshop-summary.md
The generated workshop pages cover a natural learning progression:
- Overview, introducing Air and its key features
- Your First Air App, opening the starter
app.py, running it, and viewing it in the dashboard - Building with Air Tags, replacing the simple page with styled headings, lists, and a horizontal rule to demonstrate tag nesting, attributes, and composition
- Adding Routes, creating an about page with
@app.page, a dynamic greeting page with path parameters, and navigation links between pages - Summary, recapping concepts and pointing to further learning
What the skill produced is a complete workshop with properly structured instruction pages that follow the guided experience philosophy. Learners progress through the material entirely through clickable actions. Terminal commands are executed by clicking. Files are opened, created, and modified through editor actions. The workshop configuration includes the correct YAML structure, the right session applications are enabled, and data variables are used where content needs to be parameterised for each learner's environment.
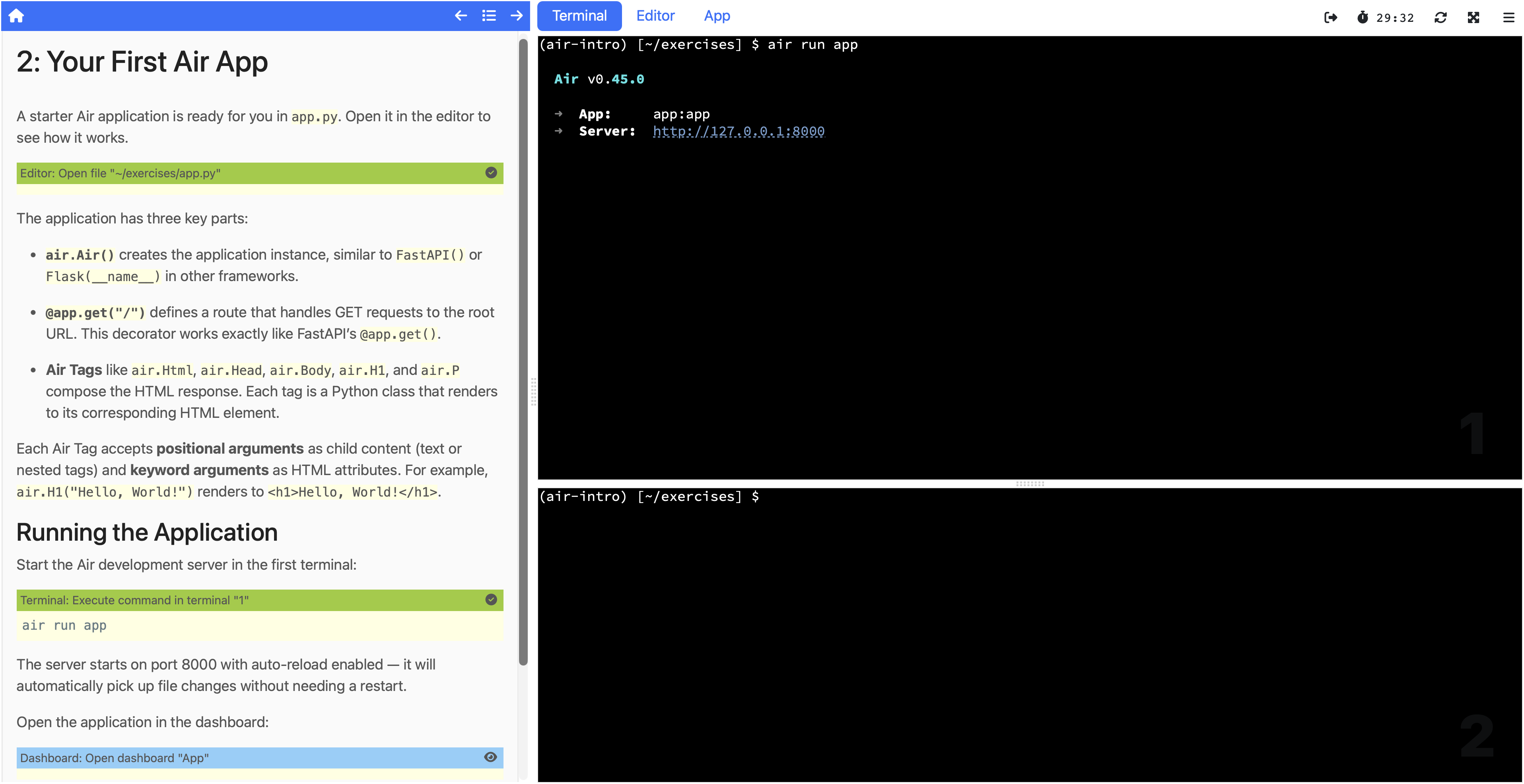
The generated content covers the progression you'd want in an introductory workshop, starting from the basics and building up to more complete applications. At each step, the explanations provide context for what the learner is about to do before the clickable actions guide them through doing it. That rhythm of explain, show, do, observe, the pattern I described in my earlier posts, is maintained consistently throughout.
Is the generated workshop perfect and ready to publish as-is? Realistically, no. Although the AI can generate some pretty amazing content, it doesn't always get things exactly right. In this case three changes were needed before the workshop would run correctly.
The first was removing some unnecessary configuration from the pyproject.toml. The generated file included settings that attempted to turn the application into an installable package, which wasn't needed for a simple workshop exercise. This isn't a surprise. AI agents often struggle to generate correct configuration for uv because the tooling has changed over time and there's plenty of outdated documentation out there that leads models astray.
The second was that the AI generated the sample application as app.py rather than main.py, which meant the air run command in the workshop instructions had to be updated to specify the application name explicitly. A small thing, but the kind of inconsistency that would trip up a learner following the steps.
The third was an unnecessary clickable action. The generated instructions included an action for the learner to click to open the editor on the app.py file, but the editor would already have been displayed by a previous action. This one turned out to be a gap in the skill itself. When using clickable actions to manipulate files in the editor, the editor tab is always brought to the foreground as a side effect. The skill didn't make that clear enough, so the AI added a redundant step to explicitly show the editor tab.
That last issue is a good example of why even small details matter when creating a skill, and also why skills have an advantage over relying purely on model training. Because the skill can be updated at any time, fixing that kind of gap is straightforward. You edit the reference material, and every future workshop generation benefits immediately. You aren't dependent on waiting for some future LLM model release that happens to have seen more up-to-date documentation.
You can browse the generated files in the sample repository on GitHub. If you check the commit history you'll see how little had to be changed from what was originally generated.
Even with those fixes, the changes were minor. The overall structure was correct, the clickable actions worked, and the content provided a coherent learning path. What would have taken hours of manual authoring to produce (writing correct clickable action syntax, getting YAML configuration right, maintaining consistent pacing across instruction pages) the skill handles all of that. A domain expert would still want to review the content, verify the technical accuracy of the explanations, and adjust the pacing or emphasis based on what they think matters most for learners. But the job shifts from writing everything from scratch to reviewing and refining what was generated.
What this means
Skills are a way of packaging expertise so that it can be reused. The knowledge I've accumulated about how to author effective Educates workshops over years of building the platform is now encoded in a form that an AI agent can apply. Someone who has never created an Educates workshop before could use this skill and produce content that follows the platform's conventions correctly. They bring the subject matter knowledge (or the AI researches it), and the skill provides the platform expertise.
That's what makes this different from just asking an AI to "write a workshop." The skill encodes not just facts about the platform but the workflow, the design principles, and the detailed reference material that turn general knowledge into correct, structured output. It's the difference between an AI that knows roughly what a workshop is and one that knows exactly how to build one for this specific platform.
Both the workshop authoring skill and the course design skill are available now, and I'm continuing to refine them as I use them. If the idea of guided, interactive workshops appeals to you, the Educates documentation is the place to start. And if you're interested in exploring the use of AI to generate workshops for Educates, do reach out to me.
February 22, 2026 12:00 AM UTC
February 21, 2026
Brett Cannon
CLI subcommands with lazy imports
In case you didn&apost hear, PEP 810 got accepted which means Python 3.15 is going to support lazy imports! One of the selling points of lazy imports is with code that has a CLI so that you only import code as necessary, making the app a bit more snappy at startup. A common example given is when you run --help you probably don&apost need all modules imported to make that work. But another use case for CLIs and lazy imports is subcommands where each subcommand very likely only needs a subset of modules to work.
How to make subcommands work with argparse
There&aposs two ways to typically do subcommands in argparse. The old-fashioned way is with a dict that dispatches to a function based on the subcommand name that was specified on the terminal. An example of that which I wrote can be found in the stdlib.

The other approach is covered in the argparse docs for subcommands which involves setting a default value for a subparser for the subcommand.
Regardless of which approach you use, the key detail is that something stores the callable you want to use based on the chosen subcommand.
Why these approaches don&apost work with lazy imports
Subcommands for a CLI is a great use of lazy imports. By making the imports that are not universally needed lazy, you can avoid paying any extra cost for imports you don&apost care about for any specific subcommand. This is even easier to do when you put a subcommand&aposs code in a separate module as you can just lazy import the main function to call in your __main__.py, e.g. lazy from spam import main as spam_main and then use spam_main as the function to call when the spam subcommand is called.
The problem is that reification (the act of making the lazy import do the actual import and become the object it&aposs meant to be) is triggered by assignment. That means using the lazy import object as a value in a dict or passing it as an argument to anything in argparse triggers the import. And since you need to do all your wiring upfront for argparse to do its thing, all of your lazy imports will get triggered that you assign using either of the approaches I listed above for making subcommands work. But I think lazy imports for subcommands is worth the hassle of trying to find a solution.
Some solutions to this problem
To make this all play nicely with lazy imports, you need to either avoid touching the lazy import objects if you don&apost need to use them or you need a level of indirection. To avoid touching the objects, you can do something like turning the dict approach into using a match statement.
match context.subcommand:
case "spam":
spam_main(context)
Another way to do it is to wrap the lazy import object in a lambda so there&aposs a layer of indirection between the object and the assigment.
parser_foo.set_defaults(func=lambda args: foo(args))
Both approaches work and keep the lazy import object from being acidentally reified.
February 21, 2026 10:37 PM UTC
Talk Python to Me
#537: Datastar: Modern web dev, simplified
You love building web apps with Python, and HTMX got you excited about the hypermedia approach -- let the server drive the HTML, skip the JavaScript build step, keep things simple. But then you hit that last 10%: You need Alpine.js for interactivity, your state gets out of sync, and suddenly you're juggling two unrelated libraries that weren't designed to work together. <br/> <br/> What if there was a single 11-kilobyte framework that gave you everything HTMX and Alpine do, and more, with real-time updates, multiplayer collaboration out of the box, and performance so fast you're actually bottlenecked by the monitor's refresh rate? That's Datastar. <br/> <br/> On this episode, I sit down with its creator Delaney Gillilan, core maintainer Ben Croker, and Datastar convert Chris May to explore how this backend-driven, server-sent-events-first framework is changing the way full-stack developers think about the modern web.<br/> <br/> <strong>Episode sponsors</strong><br/> <br/> <a href='https://talkpython.fm/sentry'>Sentry Error Monitoring, Code talkpython26</a><br> <a href='https://talkpython.fm/commandbookapp'>Command Book</a><br> <a href='https://talkpython.fm/training'>Talk Python Courses</a><br/> <br/> <h2 class="links-heading mb-4">Links from the show</h2> <div><strong>Guests</strong><br/> <strong>Delaney Gillilan</strong>: <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/delaney-gillilan-338734a8/?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >linkedin.com</a><br/> <strong>Ben Croker</strong>: <a href="https://x.com/ben_pylo?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >x.com</a><br/> <strong>Chris May</strong>: <a href="https://everydaysuperpowers.dev?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >everydaysuperpowers.dev</a><br/> <br/> <strong>Datastar</strong>: <a href="https://data-star.dev?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >data-star.dev</a><br/> <strong>HTMX</strong>: <a href="https://htmx.org?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >htmx.org</a><br/> <strong>AlpineJS</strong>: <a href="https://alpinejs.dev?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >alpinejs.dev</a><br/> <strong>Core Attribute Tour</strong>: <a href="https://data-star.dev/guide/getting_started#data-*" target="_blank" >data-star.dev</a><br/> <strong>data-star.dev/examples</strong>: <a href="https://data-star.dev/examples/?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >data-star.dev</a><br/> <strong>github.com/starfederation/datastar-python</strong>: <a href="https://github.com/starfederation/datastar-python?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >github.com</a><br/> <strong>VSCode</strong>: <a href="https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=starfederation.datastar-vscode&featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >marketplace.visualstudio.com</a><br/> <strong>OpenVSX</strong>: <a href="https://open-vsx.org/extension/starfederation/datastar-vscode?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >open-vsx.org</a><br/> <strong>PyCharm/Intellij plugin</strong>: <a href="https://plugins.jetbrains.com/plugin/26072-datastar-support?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >plugins.jetbrains.com</a><br/> <strong>data-star.dev/datastar_pro</strong>: <a href="https://data-star.dev/datastar_pro?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >data-star.dev</a><br/> <strong>gg</strong>: <a href="https://discord.gg/bnRNgZjgPh?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >discord.gg</a><br/> <strong>HTML-ivating your Django web app's experience with HTMX, AlpineJS, and streaming HTML - Chris May</strong>: <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kYV8K71pY64&t=548s" target="_blank" >www.youtube.com</a><br/> <strong>Senior Engineer tries Vibe Coding</strong>: <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_2C2CNmK7dQ" target="_blank" >www.youtube.com</a><br/> <strong>1 Billion Checkboxes</strong>: <a href="https://checkboxes.andersmurphy.com?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >checkboxes.andersmurphy.com</a><br/> <strong>Game of life example</strong>: <a href="https://example.andersmurphy.com?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >example.andersmurphy.com</a><br/> <br/> <strong>Watch this episode on YouTube</strong>: <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SFc74eFhKBY" target="_blank" >youtube.com</a><br/> <strong>Episode #537 deep-dive</strong>: <a href="https://talkpython.fm/episodes/show/537/datastar-modern-web-dev-simplified#takeaways-anchor" target="_blank" >talkpython.fm/537</a><br/> <strong>Episode transcripts</strong>: <a href="https://talkpython.fm/episodes/transcript/537/datastar-modern-web-dev-simplified" target="_blank" >talkpython.fm</a><br/> <br/> <strong>Theme Song: Developer Rap</strong><br/> <strong>🥁 Served in a Flask 🎸</strong>: <a href="https://talkpython.fm/flasksong" target="_blank" >talkpython.fm/flasksong</a><br/> <br/> <strong>---== Don't be a stranger ==---</strong><br/> <strong>YouTube</strong>: <a href="https://talkpython.fm/youtube" target="_blank" ><i class="fa-brands fa-youtube"></i> youtube.com/@talkpython</a><br/> <br/> <strong>Bluesky</strong>: <a href="https://bsky.app/profile/talkpython.fm" target="_blank" >@talkpython.fm</a><br/> <strong>Mastodon</strong>: <a href="https://fosstodon.org/web/@talkpython" target="_blank" ><i class="fa-brands fa-mastodon"></i> @talkpython@fosstodon.org</a><br/> <strong>X.com</strong>: <a href="https://x.com/talkpython" target="_blank" ><i class="fa-brands fa-twitter"></i> @talkpython</a><br/> <br/> <strong>Michael on Bluesky</strong>: <a href="https://bsky.app/profile/mkennedy.codes?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" >@mkennedy.codes</a><br/> <strong>Michael on Mastodon</strong>: <a href="https://fosstodon.org/web/@mkennedy" target="_blank" ><i class="fa-brands fa-mastodon"></i> @mkennedy@fosstodon.org</a><br/> <strong>Michael on X.com</strong>: <a href="https://x.com/mkennedy?featured_on=talkpython" target="_blank" ><i class="fa-brands fa-twitter"></i> @mkennedy</a><br/></div>
February 21, 2026 08:36 PM UTC
Django Weblog
DSF member of the month - Baptiste Mispelon
For February 2026, we welcome Baptiste Mispelon as our DSF member of the month! ⭐
 Photo by Bartek Pawlik - bartpawlik.format.com
Photo by Bartek Pawlik - bartpawlik.format.com
Baptiste is a long-time Django and Python contributor who co-created the Django Under the Hood conference series and serves on the Ops team maintaining its infrastructure. He has been a DSF member since November 2014. You can learn more about Baptiste by visiting Baptiste's website and his GitHub Profile.
Let’s spend some time getting to know Baptiste better!
Can you tell us a little about yourself? (hobbies, education, etc)
I'm a French immigrant living in Norway. In the day time I work as software engineer at Torchbox building Django and Wagtail sites. Education-wise I'm a "self-taught" (whatever that means) developer and started working when I was very young. In terms of hobbies, I'm a big language nerd and I'm always up for a good etymology fact. I also enjoy the outdoor whether it's on a mountain bike or on foot (still not convinced by this skiing thing they do in Norway, but I'm trying).
How did you start using Django?
I was working in a startup where I had built an unmaintainable pile of custom framework-less PHP code. I'd heard of this cool Python framework and thought it would help me bring some structure to our codebase. So I started rewriting our services bit-by-bit and eventually switched everything to Django after about a year.
In 2012, I bought a ticket to DjangoCon Europe in Zurich and went there not knowing anyone. It was one of the best decisions of my life: the Django community welcomed me and has given me so much over the years.
What other framework do you know and if there is anything you would like to have in Django if you had magical powers?
I've been making website for more than two decades now, so I've used my fair share of various technologies and frameworks, but Django is still my "daily driver" and the one I like the best. I like writing plain CSS, and when I need some extra bit of JS I like to use Alpine JS and/or HTMX: I find they work really well together with Django.
If I had magical powers and could change anything, I would remove the word "patch" from existence (and especially from the Django documentation).
What projects are you working on now?
I don't have any big projects active at the moment, I'm mostly working on client projects at work.
Which Django libraries are your favorite (core or 3rd party)?
My favorite Django library of all time is possibly django-admin-dracula. It's the perfect combination of professional and whimsical for me.
Other than that I'm also a big fan of the Wagtail CMS. I've been learning more and more about it in the past year and I've really been liking it. The code feels very Django-y and the community around it is lovely as well.
What are the top three things in Django that you like?
1) First of course is the people. I know it's a cliche but the community is what makes Django so special.
2) In terms of the framework, what brought me to it in the first place was its opinionated structure and settings. When I started working with Django I didn't really know much about web development, but Django's standard project structure and excellent defaults meant that I could just use things out of the box knowing I was building something solid. And more than that, as my skills and knowledge grew I was able to swap out those defaults with some more custom things that worked better for me. There's room to grow and the transition has always felt very smooth for me.
3) And if I had to pick a single feature, then I'd go for one that I think is underrated: assertQuerySetEqual(). I think more people should be using it!
What is it like to be in the Ops team?
It's both very exciting and very boring 😅
Most of the tasks we do are very mundane: create DNS records, update a server, deploy a fix. But because we have access and control over a big part of the infrastructure that powers the Django community, it's also a big responsibility which we don't take lightly.
I know you were one of the first members of the Django Girls Foundation board of directors. That's amazing! How did that start for you?
By 2014 I'd become good friend with Ola & Ola and in July they asked me to be a coach at the very first Django Girls workshop at EuroPython in Berlin. The energy at that event was amazing an unlike any other event I'd been a part of, so I got hooked.
I went on to coach at many other workshops after that. When Ola & Ola had the idea to start an official entity for Django Girls, they needed a token white guy and I gladly accepted the role!
You co-created Django Under the Hood series which, from what I've heard, was very successful at the time. Can you tell us a little more about this conference and its beginnings?
I'm still really proud of having been on that team and of what we achieved with this conference. So many stories to tell!
I believe it all started at the Django Village conference where Marc Tamlin and I were looking for ideas for how to bring the Django core team together.
We thought that having a conference would be a good way to give an excuse (and raise funds) for people to travel all to the same place and work on Django. Somehow we decided that Amsterdam was the perfect place for that.
Then we were extremely lucky that a bunch of talented folks actually turned that idea into a reality: Sasha, Ola, Tomek, Ola, Remco, Kasia (and many others) 💖.
As a former conference organizer and volunteer, do you have any recommendations for those who want to contribute or organize a conference?
I think our industry (and even the world in general) is in a very different place today than a decade ago when I was actively organizing conferences. Honestly I'm not sure it would be as easy today to do the things we've done.
My recommendation is to do it if you can. I've forged some real friendships in my time as an organizer, and as exhausting and stressful as it can be, it's also immensely rewarding in its own way.
The hard lesson I'd also give is that you should pay attention to who gets to come to your events, and more importantly who doesn't. Organizing a conference is essentially making a million decisions, most of which are really boring. But every decision you make has an effect when it's combined with all the others. The food you serve or don't serve, the time of year your event takes place, its location. Whether you spend your budget on fun tshirts, or on travel grants.
All of it makes a difference somehow.
Do you remember your first contribution in Django?
I do! It was commit ac8eb82abb23f7ae50ab85100619f13257b03526: a one character typo fix in an error message 😂
Is there anything else you’d like to say?
Open source is made of people, not code. You'll never go wrong by investing in your community. Claude will never love you back.
Thank you for doing the interview, Baptiste !
February 21, 2026 09:11 AM UTC
PyBites
3 Questions to go from thinking like a Scrappy to Senior Dev
How do you know if you’re actually growing as a dev?
Last week I was chatting with a developer who’d hit a wall. (I talk to a lot of devs now that I think about it!)
Like him, you might consider yourself a scrappy coder. You’re an all-rounder, can generally figure things out and write some sort of scrappy script to solve a problem.
It’s actually a badge of pride! I myself have a bunch of scrappy scripts running in my home lab to do various things.
The thing is, sometimes this confidence we feel being scrappy, may actually just be comfort.
For this dev, he was comfortable fixing bugs, but the idea of staring at a blank file and architecting an end-to-end solution from scratch scared the pants off him.
It was this form of “engineering” that he just couldn’t get down.
The chat inspired me to create 3 things you can check today to push yourself out of this scrappy zone and into the realm of senior development/engineering.
Have a look at a function or codebase you’ve written and ask:
- “Is this deliberate?” Did I write it this way because it’s the best way, or because it’s the first way I found on Google that didn’t crash?
Senior developers are intentional in the code they write. - “How do I prove this works?” If I had to write a test for this right now, could I? Are you writing tests for your code? If not, how come? Your code should be straightforward enough that you can write tests for it.
- “What happens if I leave?” If I disappeared tomorrow, would the next developer thank me or curse my soul?
This forces you to think about readability, context managers, and structure (like using uv or proper config files) rather than hard-coding values just to get it done.
These are simple questions that have real impact when you start considering them as you write code. You’ll be surprised how much more robust your applications become!
Try asking these three questions today. If it’s uncomfortable, good! That means you’re growing!
And when you’re ready to take the next step on your Python journey, (shameless plug incoming), click the link below to chat with us about 1:1 Coaching. We’ll help you get there!
Julian
This was originally sent to our email list. Join here.
February 21, 2026 09:00 AM UTC
Graham Dumpleton
Clickable actions in workshops
The idea of guided instruction in tutorials isn't new. Most online tutorials these days provide a click-to-copy icon next to commands and code snippets. It's a useful convenience. You see the command you need to run, you click the icon, and it lands in your clipboard ready to paste. Better than selecting text by hand and hoping you got the right boundaries.
But this convenience only goes so far. The instructions still assume you have a suitable environment set up on your own machine. The commands might reference tools you haven't installed, paths that don't exist in your setup, or configuration that differs from what the tutorial expects. The copy button solves the mechanics of getting text into your clipboard, but the real friction is in the gap between the tutorial and your environment. You end up spending more time troubleshooting your local setup than actually learning the thing the tutorial was supposed to teach you.
Hosted environments and the copy/paste problem
Online training platforms like Instruqt and Strigo improved on this by providing VM-based environments that are pre-configured and ready to go. You don't need to install anything locally. The environment matches what the instructions expect, so commands and paths should work as written. That eliminates the entire class of problems around "works on the tutorial author's machine but not on mine."
The interaction model, though, is still copy and paste. You read instructions in one panel, find the command you need, copy it, switch to the terminal panel, paste it, and run it. For code changes, you copy a snippet from the instructions and paste it into a file in the editor. It works, but it's a manual process that requires constant context switching between panels. Every copy and paste is a small interruption, and over the course of a full workshop those interruptions add up. Learners end up spending mental energy on the mechanics of following instructions rather than on the material itself.
When commands became clickable
Katacoda, before it was shut down by O'Reilly in 2022, included an improvement to this model. Commands embedded in the workshop instructions were clickable. Click on a command and it would automatically execute in the terminal session provided alongside the instructions. No copying, no pasting, no switching between panels. The learner reads the explanation, clicks the command, and watches the result appear in the terminal. The flow from reading to doing became much more seamless.
This was a meaningful step forward for terminal interactions specifically. But it only covered one part of the workflow. For code changes, editing configuration files, or any interaction that involved working with files in an editor, you were still back to the copy and paste model. The guided experience had a gap. Commands were frictionless, but everything else still required manual effort.
Educates and the fully guided experience
Educates takes the idea of clickable actions and extends it across the entire workshop interaction. The workshop dashboard provides instructions alongside live terminals and an embedded VS Code editor. Throughout the instructions, learners encounter clickable actions that cover not just running commands, but the full range of things you'd normally do in a hands-on technical workshop.
Terminal actions work the way Katacoda relied on. Click on a command in the instructions and it runs in the terminal. But Educates goes further by providing a full set of editor actions as well. Clickable actions can open a file in the embedded editor, create a new file with specified content, select and highlight specific text within a file, and then replace that selected text with new content. You can append lines to a file, insert content at a specific location, or delete a range of lines. All of it driven by clicking on actions in the instructions rather than manually editing files.
Educates also includes YAML-aware editor actions, which is significant because YAML editing is notoriously error-prone when done by hand. A misplaced indent or a missing space after a colon can break an entire configuration file, and debugging YAML syntax issues is not what anyone signs up for in a workshop about Kubernetes or application deployment. The YAML actions let you reference property paths like spec.replicas or spec.template.spec.containers[name=nginx] and set values, add items to sequences, or replace entries, all while preserving existing comments and formatting in the file.
Beyond editing, Educates provides examiner actions that run validation scripts to check whether the learner has completed a step correctly. In effect, the workshop can grade the learner's work and provide immediate feedback. If they missed a step or made an error, they find out right away rather than discovering it three steps later when something else breaks. There are also collapsible section actions for hiding optional content or hints until the learner needs them, and file transfer actions for downloading files from the workshop environment to the learner's machine or uploading files into it.
The end result is that learners can progress through an entire workshop without ever manually typing a command, editing a file by hand, or wondering whether they've completed a step correctly. They focus on understanding the concepts being taught while the clickable actions handle the mechanics. That changes the experience fundamentally. Instead of the workshop being something you push through, it becomes something that carries you forward.
The dashboard in action
To get a sense for what this looks like in practice, here are a couple of screenshots from an Educates workshop.
The instructions panel on the left contains a clickable action for running a command. When the learner clicks it, the command executes in the terminal panel and the output appears immediately. No copying, no pasting, no typing.
Here the embedded editor shows the result of a select-and-replace flow. The instructions guided the learner through highlighting specific text in a file and then replacing it with updated content, all through clickable actions. The learner sees exactly what changed and why, without needing to manually locate the right line and make the edit themselves.
How it works in the instructions
Workshop instructions in Educates are written in markdown. Clickable actions are embedded as specially annotated fenced code blocks where the language identifier specifies the action type and the body contains YAML configuration that controls what the action does.
For example, to guide a learner through updating an image reference in a Kubernetes deployment file, you might include two actions in sequence. The first selects the text that needs to change:
```editor:select-matching-text
file: ~/exercises/deployment.yaml
text: "image: nginx:1.19"
```
The second replaces the selected text with the new value:
```editor:replace-text-selection
file: ~/exercises/deployment.yaml
text: "image: nginx:latest"
```
When the learner clicks the first action, the matching text is highlighted in the editor so they can see exactly what will change. When they click the second, the replacement is applied. They understand the change being made because they see both the before and after states, but they don't need to manually find the right line, select the text, and type the replacement. The instructions guide them through it.
For terminal commands, the syntax is even simpler:
```terminal:execute
command: |-
echo "Hello from terminal:execute"
```
The YAML within each code block controls everything about the action: which file to operate on, what text to match or replace, which terminal session to use, and so on. The format is consistent across all action types. Once you understand the pattern of action type as the language identifier and YAML configuration as the body, authoring with actions is straightforward.
The value of removing friction
The progression from copy/paste tutorials to hosted environments to clickable commands to a fully guided experience like Educates is ultimately a progression toward removing every point where a learner might disengage. Each improvement eliminates another source of friction, another moment where someone might lose focus because they're fighting the tools instead of learning the material. When the mechanics of following instructions become invisible, learners stay engaged longer and absorb more of what the workshop is trying to teach.
In my previous post I discussed how this interactive format, combined with thoughtful use of AI for content generation, can produce workshop content that maintains consistent quality throughout. The clickable actions I've described here are what make that format possible. They're the mechanism that turns static instructions into a guided, interactive experience where the learner's attention stays on the concepts rather than the process.
In future posts I plan to write about how I'm using AI agent skills to automate the creation of Educates workshops, including the generation of all the clickable actions that drive the guided process along with the commentary and explanations the workshop instructions include. The goal is that the generated workshop runs out of the box, with the only remaining step being for the domain expert to validate the content and tweak where necessary. That has the potential to save a huge amount of time in creating workshops, making it practical to build high-quality guided learning experiences for topics that would otherwise never get the investment.
February 21, 2026 12:00 AM UTC
February 20, 2026
Real Python
The Real Python Podcast – Episode #285: Exploring MCP Apps & Adding Interactive UIs to Clients
How can you move your MCP tools beyond plain text? How do you add interactive UI components directly inside chat conversations? This week on the show, Den Delimarsky from Anthropic joins us to discuss MCP Apps and interactive UIs in MCP.
[ Improve Your Python With 🐍 Python Tricks 💌 – Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. >> Click here to learn more and see examples ]